Spunbond Nonwoven Industry Overview
The global spunbond nonwoven market size was estimated at USD 13.88 billion in 2019 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4% from 2020 to 2027. Increasing birth rate and rising awareness about the benefits of the use of baby diapers expected to drive market growth.
Increase in use of spunbond nonwovens for geotextiles is expected to have a positive impact on the demand. Growing number of transportation infrastructure planners, builders, and engineers, are adopting geotextiles as durable material for highways, roads, railways, and foundations. Geotextiles are gaining demand in new applications such as mining, oil drilling sites, shale gas, providing further opportunities.
Gather more insights about the market drivers, restrains and growth of the Spunbond Nonwoven Market
The market in China is expected to exhibit high growth on account of the rapid development of application industries. The market exhibits high production volumes of pharmaceutical and textile products thereby accounting for high product consumption. The presence of a robust textile industry in the region is expected to emerge as one of the prominent growth drivers for the market.
Several regulations have been enforced for the production of and use of spunbond nonwoven in various application industries. Use of spunbond nonwovens for food packaging application is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). In addition, FDA and European counsel have also approved the use of spunbond nonwovens in medical and healthcare applications.
Spunbond is the second largest process used for the processing of sustainable nonwovens, due to cost-effectiveness and high performance. Spunbond process yields higher output at comparatively lower costs. Due to lack sustainability in wet-laid process, many companies are replacing wet-laid process with spunbond process.
However, frequent fluctuations in raw material prices may hamper the growth of the spunbond nonwoven market. Polymers are an important raw material for the production of spunbond nonwovens. Polypropylene is the most widely used polymer, accounting for more than 50% of the total raw material share. Prices of polymers generally follow oil prices. Hence, any movement can result into volatility of oil prices, which in turn affects polymer prices.
Browse through Grand View Research's Smart Textiles Industry Research Reports.
- The global personal protective equipment market size was over USD 79.53 billion in 2023and is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 7.2% from 2024 to 2030.
- The global ballistic protective equipment market size was estimated at USD 4.80 billion in 2023and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.0% from 2024 to 2030.
Spunbond Nonwoven Market Segmentation
Grand View Research has segmented the global spunbond nonwoven market on the basis of material, product, application, and region:
Spunbond Nonwoven Material Outlook (Volume, Kilotons; Revenue, USD Million, 2016 - 2027)
- Polypropylene
- Polyester
- Polyethylene
- Others
Spunbond Nonwoven Product Outlook (Volume, Kilotons; Revenue, USD Million, 2016 - 2027)
- Disposable
- Durable
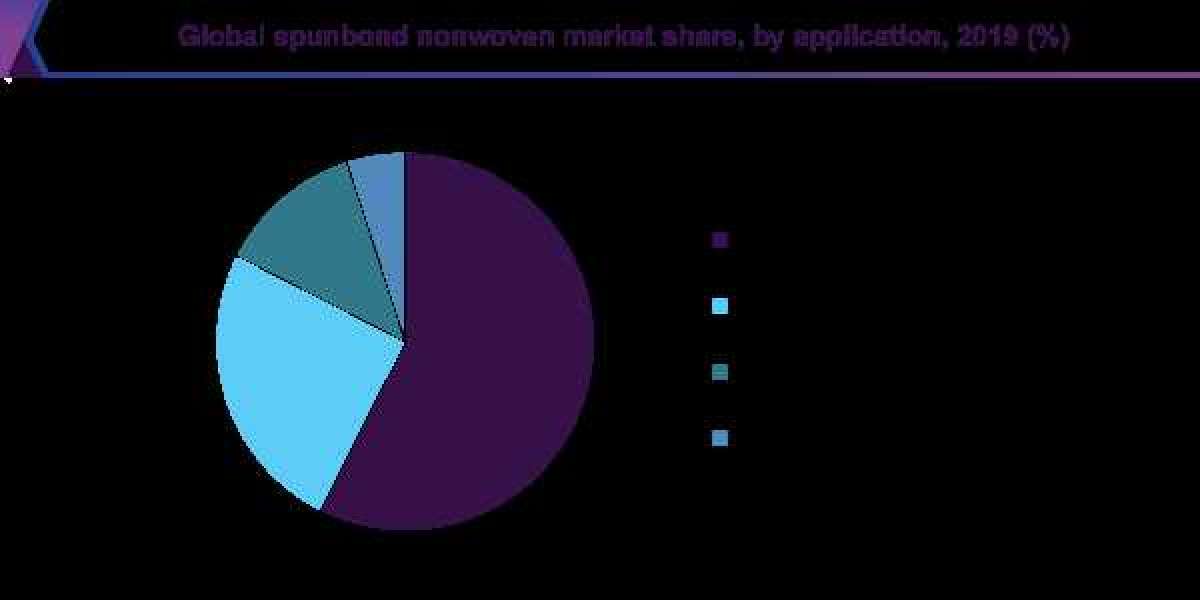
Spunbond Nonwoven Application Outlook (Volume, Kilotons; Revenue, USD Million, 2016 - 2027)
- Personal Hygiene
- Medical Healthcare
- Geotextiles
- Others
Spunbond Nonwoven Regional Outlook (Volume, Kilotons; Revenue, USD Million, 2016 - 2027)
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Germany
- U.K.
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- Central South America
- Brazil
- Middle East Africa
Key Companies profiled:
- Freudenberg Group
- DuPont
- Ahlstrom-Munksjo Oyj
- Komberly-Clark Corporation
- Berry Global Group, Inc.
- FITESA
- Johns Manville Corporation
- Toray Industries
- Indorama Ventures
- Pegas Nonwovens S.A.
- Akitieselskabet Schouw Co.
- Asahi Kasai Corporation
- Mitsui Chemicalsa
Order a free sample PDF of the Spunbond Nonwoven Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.